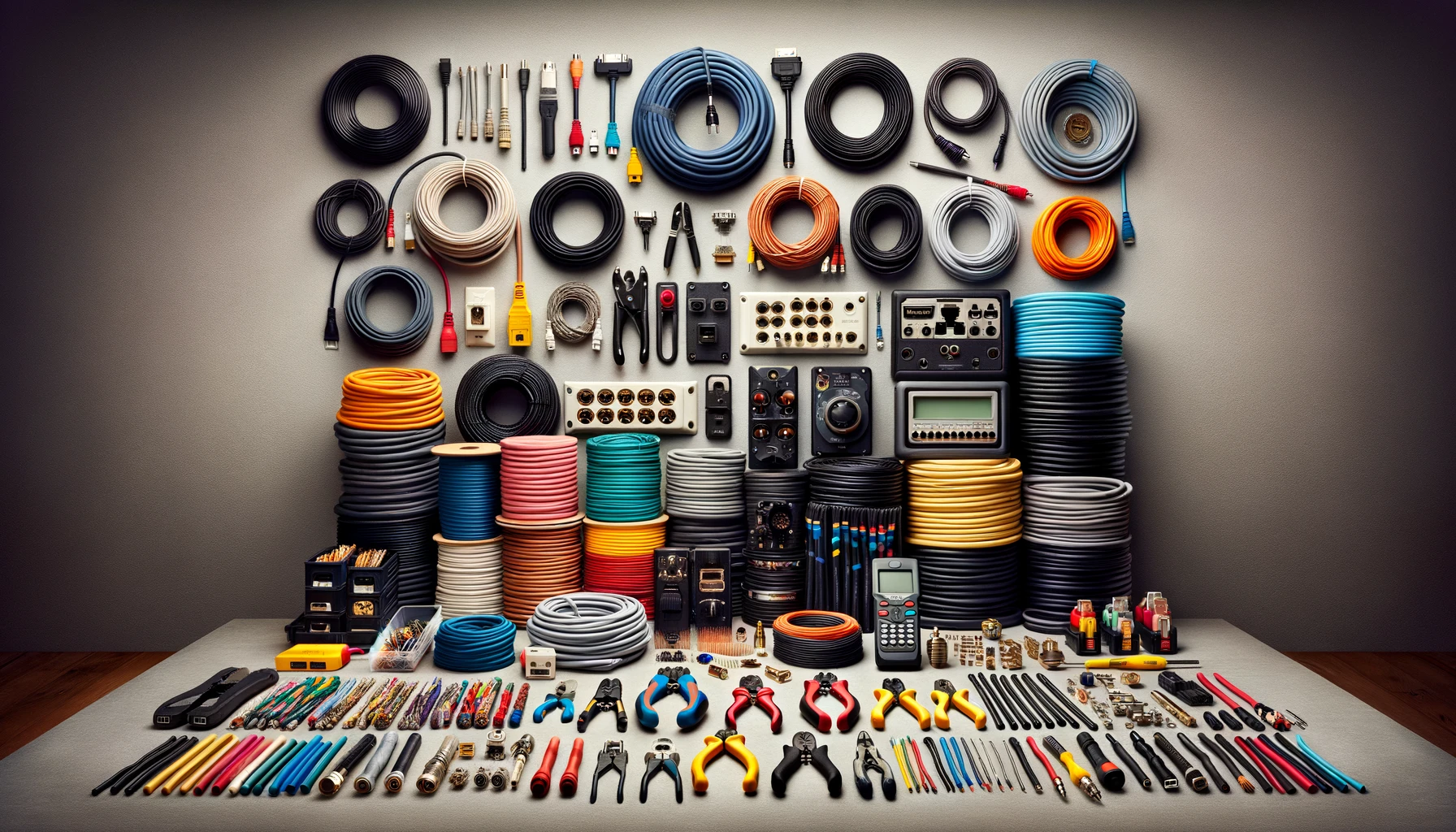
I. Introduction
Navigating through the complexities of alarm cables, HDMI cables, ethernet cables, and more can be a daunting task for even the most tech-savvy individuals. Each type of cable comes with its unique set of characteristics, advantages, and suitable applications, making it crucial to understand their differences and functionalities. Whether you're setting up a new home entertainment system, wiring a building for telecommunications, or installing a state-of-the-art security system, this guide will walk you through the essentials of cable selection, ensuring optimal performance and seamless connectivity for all your devices.
II. From Sound Cables to Security Cables
Alarm cables are the unsung heroes in the realm of security systems, providing the critical link between sensors, control panels, and alarms. These cables are specifically designed to facilitate the reliable transmission of signals in intruder alarm systems, CCTV, access control, and fire alarm setups. Opting for the right alarm cable is crucial, as it directly impacts the system's responsiveness and effectiveness. Typically, these cables come in both screened (shielded) and unscreened varieties, with screened cables offering additional protection against electromagnetic interference, ensuring that the signal remains clear and uninterrupted over longer distances.
The construction of alarm cables often involves multiple cores, allowing them to carry power, data, and control signals simultaneously. This multi-core design not only simplifies the installation process by reducing the number of cables needed but also enhances the overall efficiency and reliability of the security system. When selecting an alarm cable, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of your security system, including the length of the cable runs and the potential for electromagnetic interference in the environment. This ensures that the chosen cable provides a stable and secure connection, crucial for maintaining the integrity of your security infrastructure.
Moreover, the choice between PVC and Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) insulation materials can also play a significant role, especially in environments where safety and reduction of toxic emissions in the event of a fire are paramount. LSZH cables are particularly suited to public buildings and confined spaces, offering an extra layer of safety. Ultimately, the correct selection of alarm cables not only supports the seamless operation of security systems but also contributes to the safety and protection of properties, assets, and individuals.
Bell cables are integral to the installation and operation of doorbell systems, intercoms, and similar communication devices within both residential and commercial properties. These cables are engineered to deliver low-voltage power and signal transmission with reliability and clarity, ensuring that doorbell chimes, buzzers, and intercom speakers function seamlessly. The simplicity of bell cables belies their importance; a properly chosen and installed bell cable can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of your communication system, providing clear audio transmission without interference.
When selecting bell cables, it’s essential to consider the distance between the bell push and the chime or intercom unit, as well as any potential sources of electrical interference. For most domestic installations, standard bell cables offer sufficient performance, ensuring that doorbell systems operate effectively without any noticeable delay or distortion. However, in more complex systems or in environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference, shielded bell cables may be necessary to preserve signal integrity and prevent crosstalk with other nearby electrical systems.
Additionally, the choice of bell cable should also take into account the environmental conditions it will be exposed to. For external runs or installations in areas prone to moisture, cables with enhanced insulation or weatherproofing features are advisable to prevent degradation and ensure longevity. By carefully selecting the right type of bell cable for your specific needs, you can ensure reliable and efficient operation of your doorbell or intercom system, maintaining clear communication at the entrance of your home or business.
Heating cables, also known as heat trace cables or underfloor heating cables, play a pivotal role in providing targeted warmth in a variety of settings, from preventing pipes from freezing in the winter to adding comfort under tile flooring. These cables work by converting electrical energy into heat, a process controlled through built-in thermostats or external control systems to maintain desired temperature levels. The versatility of heating cables allows them to be used in both residential and commercial applications, offering an efficient solution to meet diverse heating needs.
When selecting heating cables, it's essential to consider the specific application to ensure optimal performance. For example, underfloor heating installations require cables that can distribute heat evenly and are compatible with the flooring material, whereas pipe freeze protection might need cables with self-regulating capabilities to adjust heat output according to the external temperature. This adaptability not only ensures the comfort and safety of the environment but also contributes to energy efficiency, reducing unnecessary power consumption by adapting to the actual heating requirements.
Moreover, the installation of heating cables requires careful planning and adherence to safety standards to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability. Whether embedding them within floors or wrapping them around pipes, it’s crucial to select the right type of cable and install it correctly, following manufacturer guidelines. With their ability to provide precise heating where and when it's needed, heating cables offer a smart and flexible approach to temperature management, enhancing the functionality and comfort of spaces while optimizing energy use.
Telephone cables are essential for the infrastructure of both residential and commercial communication networks, facilitating the transmission of voice and data signals over distances. These cables come in various types, including traditional twisted pair cables for landline telephone systems and newer, more advanced options designed for digital and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) technologies. The correct selection of telephone cable is crucial for ensuring clear, reliable communication without interference or signal loss.
For traditional telephone systems, twisted pair cables, which consist of pairs of insulated wires twisted together, help reduce electromagnetic interference and maintain signal integrity. In environments where multiple telephone lines are required, multi-pair cables with up to hundreds of individual pairs can be used, making them ideal for office buildings or telecommunication hubs. On the other hand, installations that support digital or VoIP telephony may benefit from higher-grade cables, such as Category 5e or Category 6 Ethernet cables, which can handle the increased data rates necessary for digital communication.
When planning a telephone system installation or upgrade, it’s important to consider not only the current needs but also future scalability. With the evolving landscape of communication technology, opting for cables that provide ample bandwidth and support for emerging technologies can save time and resources in the long run. Whether for a simple home telephone line or a complex commercial telecommunication system, choosing the right telephone cable lays the foundation for effective and efficient communication.
Speaker cables are a critical component in any audio system, responsible for delivering sound signals from amplifiers to speakers with minimal loss or distortion. The quality and type of speaker cable can significantly impact the audio clarity and overall performance of the system, making it vital to choose cables that match the specifications of both the speakers and the amplifier. These cables typically consist of two insulated conductors that ensure the positive and negative signals are kept distinct, preserving the integrity of the audio signal.
The gauge (thickness) of the speaker wire is an important consideration, as it affects the cable's resistance and, consequently, the sound quality, especially over longer distances. Thicker cables (lower gauge numbers) have less resistance and are preferred for longer runs or high-power applications, ensuring that the audio signal remains strong and clear from source to output. Conversely, for shorter connections or lower-powered systems, thinner cables (higher gauge numbers) can be sufficient and more cost-effective.
In addition to gauge, the material of the conductor (typically copper or silver) plays a role in the cable's performance, with each offering different benefits in terms of conductivity and sound quality. Copper is widely used due to its excellent conductivity and affordability, while silver, though more conductive, is often reserved for high-end audio applications due to its higher cost. When setting up or upgrading an audio system, investing in quality speaker cables that suit the system's requirements can enhance the listening experience, ensuring rich, detailed sound reproduction.
Screened cables, also known as shielded cables, are designed to protect signal integrity against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This interference can significantly degrade the performance of electrical and electronic systems, leading to data corruption, signal loss, and operational disruptions. The screening, typically made of metallic foil or braided wire, acts as a barrier that encases the core conductors, reflecting or absorbing external interference and preventing it from affecting the signal.
The application of screened cables is crucial in environments where electrical equipment and devices operate in close proximity, and where interference can cause critical failures or inaccuracies. This includes industrial settings, data centres, medical facilities, and audio-visual installations. By ensuring that signals are transmitted clearly and without external noise, screened cables play a pivotal role in maintaining the reliability and accuracy of communication and data transmission systems.
Choosing the right type of screened cable involves considering the specific demands of the application, including the types of devices involved, the level of interference expected, and the environmental conditions. For instance, foil shielding is often used for high-frequency applications, while braided shielding is preferred for its durability and effectiveness at lower frequencies. Proper installation and grounding of screened cables are also essential to maximise their effectiveness in interference mitigation, making them indispensable in maintaining optimal performance in complex electrical and electronic systems.
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) cables have become the standard for transmitting high-definition video and audio signals between devices in both residential and commercial settings. These cables are capable of delivering clear, uncompressed digital signals for a range of applications, from home entertainment systems connecting televisions and audio receivers to professional setups linking projectors and monitors in conference rooms. HDMI cables support various video formats, including standard, enhanced, high-definition, and ultra-high-definition (4K and 8K), making them versatile for multimedia requirements.
One of the key advantages of HDMI cables is their ability to carry both audio and video signals through a single connection, simplifying the setup and reducing cable clutter. Additionally, newer versions of HDMI cables offer enhanced features such as Ethernet data connectivity, allowing connected devices to share an internet connection, and ARC (Audio Return Channel), which enables the TV to send audio back to an audio system without the need for separate audio cables.
When selecting an HDMI cable, it's important to consider the specific needs of your setup, such as the required length, the HDMI version compatibility (e.g., HDMI 2.0, HDMI 2.1), and whether advanced features like Ethernet or ARC are needed. With the right HDMI cable, users can ensure seamless transmission of high-quality video and audio, enhancing the viewing or presentation experience with vivid visuals and clear sound.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) cables are pivotal in the realm of data transfer and device charging, connecting an extensive array of devices including computers, smartphones, cameras, and more. These cables have evolved through various iterations, from USB 1.1 to the latest USB-C, each version offering improvements in data transfer speeds, power delivery, and connectivity options. USB cables facilitate not only the transfer of data but also the charging of devices, making them a versatile tool in both personal and professional settings.
The introduction of USB-C has marked a significant advancement in USB technology, featuring a reversible, symmetrical design that eliminates the common frustration of incorrect cable orientation. USB-C cables support faster data transfer rates and a higher power flow, enabling quicker charging times and the ability to power larger devices, such as laptops, which previously relied on proprietary chargers. This universal approach aims to simplify cable requirements and enhance user experience across a broad spectrum of devices.
When choosing a USB cable, it’s crucial to match the cable type with the device's specifications to ensure compatibility and optimise performance. For example, while a USB 2.0 cable might suffice for basic data transfer or charging needs, tasks requiring higher bandwidth or power, such as connecting an external hard drive or fast-charging a modern smartphone, would benefit from the capabilities of USB 3.0 or USB-C cables. The correct selection of a USB cable not only ensures efficient and reliable connectivity but also supports the seamless operation and interaction of a wide variety of devices in today’s interconnected digital landscape.
Ethernet cables form the backbone of wired network connections, offering a reliable and secure method for connecting devices to the internet and each other. Predominantly used in both home and office networks, these cables facilitate high-speed data transmission, making them indispensable for internet access, file sharing, and streaming services. Variants such as Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7 differ in their maximum data transfer speeds and bandwidth capabilities, allowing users to choose based on their specific networking requirements.
Cat6 cables, for example, are popular for their ability to support Gigabit Ethernet speeds, which are essential for high-demand applications such as video conferencing, online gaming, and HD video streaming. The advancement to Cat6a and Cat7 cables offers even higher speeds and bandwidth, reducing latency and improving network performance for critical business applications and data centres that handle large volumes of data.
When setting up a network, the choice of Ethernet cable can significantly impact overall performance. Factors to consider include the length of cable needed, as longer runs may require higher quality cables to prevent signal degradation, and the environment in which the cable will be used, as some are designed with shielding to protect against electromagnetic interference. By carefully selecting the appropriate Ethernet cable, users can ensure a stable and fast network connection, optimising their online experience and productivity.
Coaxial cables are widely used for transmitting radio frequency (RF) signals, making them a staple in television systems, broadband internet connections, and in the field of telecommunications. Characterised by their concentric design, which includes an inner conductor, insulating layer, metallic shield, and an outer plastic sheath, coaxial cables are engineered to minimize electromagnetic interference, ensuring clear signal transmission over distances.
The versatility of coaxial cables extends to various applications, from connecting satellite dishes and antennas to TVs, to linking computers to broadband internet services. Their ability to carry a wide range of frequencies with minimal loss makes them particularly valuable in environments where signal integrity is paramount. Coaxial cables come in different types, such as RG6 and RG11, with each type suited to specific applications based on signal strength and distance requirements.
When choosing a coaxial cable, it's crucial to consider the specific needs of your setup, such as the required length of the cable run and the level of signal quality needed. For instance, RG6 cables are commonly used in residential internet and cable TV installations for their balance between flexibility and performance, while RG11 cables are preferred for longer distances or outdoor use due to their thicker design and lower signal loss. Selecting the right coaxial cable ensures optimal performance of your TV, internet, or communication systems, providing reliable and high-quality connectivity.
VGA (Video Graphics Array) cables have been a foundational component in connecting computers to monitors and projectors, facilitating the transmission of analog video signals. Despite the emergence of digital interfaces like HDMI and DisplayPort, VGA cables remain relevant in many settings due to their widespread compatibility and simplicity. They are particularly valued in environments where legacy hardware is still operational, ensuring that older devices can still function effectively in modern workflows.
A VGA cable typically consists of a 15-pin connector on each end, capable of supporting resolutions up to 640x480 in 16 colors or 320x200 in 256 colors, which was considered high-resolution at the time of VGA’s inception. While these specifications might seem modest by today’s standards, VGA technology has evolved, with enhanced versions supporting higher resolutions, making it possible to use VGA connections for a variety of applications that do not require the highest video quality.
When considering the use of VGA cables for video connections, it’s important to note the limitations in terms of resolution and color depth compared to digital alternatives. However, their analog nature allows for flexibility in cable length without significant loss of signal quality, a factor that can be crucial in setups requiring long cable runs. For those looking to connect older computers or video equipment to displays, VGA cables offer a reliable, albeit less technologically advanced, solution to meet their needs.
Power cables are fundamental components of any electrical system, tasked with the distribution of electricity from the power source to various devices and machinery. Available in a vast array of types and specifications, they cater to a broad spectrum of power needs, from simple household appliances to complex industrial machinery. The selection of the appropriate power cable is critical, depending on the voltage requirement, current carrying capacity, and environmental conditions in which the cable will operate. This ensures not only the efficient and safe transmission of electrical power but also the longevity and reliability of both the cable and the equipment it powers.
In residential settings, power cables must comply with safety standards and building regulations, often encapsulated within protective sheathing to prevent damage and protect users. In industrial environments, power cables might need additional features such as armouring for mechanical protection or special insulation materials to withstand harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures. The choice between single-core and multi-core cables, as well as the determination of the appropriate gauge and insulation type, is guided by both the application's specific requirements and the need to minimize power loss over distance.
Moreover, the installation of power cables demands careful planning and adherence to stringent installation codes to prevent hazards such as electrical fires or shock. Properly selected and installed power cables not only facilitate the smooth operation of various systems but also contribute to energy efficiency by reducing losses and preventing downtime caused by cable failure. As technology advances, the development of more durable, efficient, and environmentally friendly power cables continues to evolve, aiming to meet the growing demands of modern electrical and electronic applications.
The successful installation and maintenance of cable systems, whether for data, audio-visual, or power applications, require the right set of cable tools. These tools not only ensure that installations are performed efficiently and safely but also that the integrity of the cable is preserved, guaranteeing optimal performance. From wire strippers and crimping tools to cable testers and punch-down tools, each plays a vital role in preparing and securing cables for their specific uses.
Wire strippers are indispensable for cleanly removing the insulation from cables without damaging the internal wires, a crucial step in creating connections that are both secure and conductive. Crimping tools, on the other hand, are used to attach connectors to the ends of cables, such as RJ45 plugs on Ethernet cables or coaxial connectors, ensuring a tight and reliable connection that is essential for signal integrity. Meanwhile, cable testers are crucial for troubleshooting and verifying the functionality of cable connections, helping to identify issues such as shorts, open circuits, or incorrect wiring configurations.
For those working with structured cabling systems, punch-down tools enable the insertion of individual wires into patch panels and keystone jacks, creating a neat and organized setup that is easy to manage. Investing in high-quality cable tools is not just about facilitating the installation process; it's about ensuring the reliability and longevity of the cable system. With the right tools at hand, professionals and enthusiasts alike can achieve installations that meet high standards of quality and performance, underpinning the success of any cable-based system.
III. Conclusion
In conclusion, the diverse world of cables plays a pivotal role in connecting and powering our modern world, from the simplest of home appliances to the most complex data centers and industrial machinery. Understanding the specific types of cables, such as alarm, bell, heating, telephone, speaker, screened, HDMI, USB, Ethernet, coaxial, VGA, and power cables, alongside the essential tools required for their installation, is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, safety, and reliability of both residential and commercial systems. Each cable type serves a unique purpose, catering to specific requirements and environments, underscoring the importance of selecting the right cable for the right application.
As technology continues to advance, the need for more sophisticated cabling solutions will inevitably grow. Staying informed about the latest developments in cable technology and best practices in installation will enable both professionals and enthusiasts to make informed decisions, ensuring that their systems are not only up to current standards but also future-proofed against upcoming advancements. Whether for power, data, or audio-visual needs, the right cables, when chosen and installed correctly, form the lifelines of our increasingly interconnected world.